Understanding the Risk-Reward Ratio in Trading: A Key Metric for Successful Decision-making
In the world of trading, where profitability is the ultimate goal, understanding and managing risk is of paramount importance. One tool that traders rely on to assess the potential gains versus the potential losses of a trade is the risk-reward ratio. The risk-reward ratio is a fundamental metric that helps traders make informed decisions and evaluate the potential profitability of their trades. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the risk-reward ratio, its calculation, and its significance in trading.
Defining the Risk-Reward Ratio
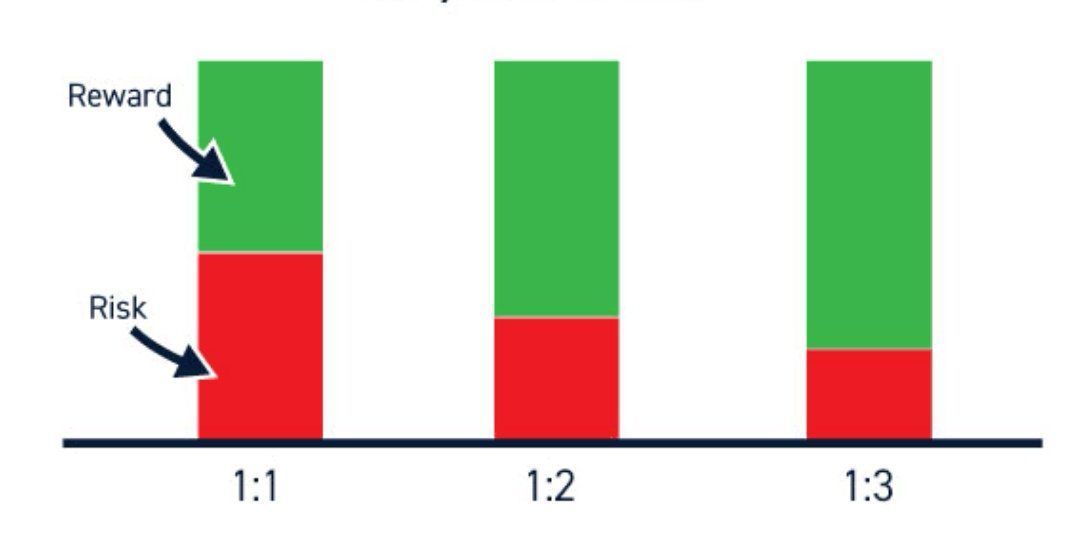
The risk-reward ratio is a numerical representation of the potential risk (downside) and reward (upside) of a trade. It measures the ratio between the amount of capital a trader is willing to risk on a trade (risk) and the expected profit they anticipate to gain if the trade is successful (reward). By calculating and comparing these two components, traders can assess the viability of a trade and determine if the potential reward justifies the associated risks.
Calculating the Risk-Reward Ratio
To calculate the risk-reward ratio, traders need to identify two essential parameters: the stop-loss level and the take-profit level. The stop-loss is the predetermined price at which a trader will exit the trade to limit their potential losses, while the take-profit is the target price at which they will exit the trade to secure their anticipated profits. Once these levels are established, the risk-reward ratio is calculated by dividing the potential loss (distance between entry and stop-loss) by the potential profit (distance between entry and take-profit).
Example
Let's consider a hypothetical trade where a trader enters a position at $100 and sets a stop-loss at $95. If the trader's take-profit level is set at $115, the potential loss would be $5 (entry price minus stop-loss), and the potential profit would be $15 (take-profit price minus entry). Therefore, the risk-reward ratio for this trade would be 1:3, indicating that the potential profit is three times greater than the potential loss.
Significance of the Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio serves as a crucial tool in risk management and decision-making for traders. Here's why it is significant:
1. Assessing trade viability: By comparing the potential reward to the potential risk, traders can determine if a trade is worth pursuing. A favorable risk-reward ratio suggests that the potential profits outweigh the potential losses, making the trade more appealing.
2. Setting realistic profit targets: The risk-reward ratio helps traders set realistic take-profit levels based on their risk tolerance and market conditions. It encourages traders to aim for profit levels that are proportionate to the risks they are taking.
3. Controlling risk exposure: By evaluating the risk-reward ratio, traders can manage their risk exposure effectively. Trades with unfavorable risk-reward ratios can be avoided or adjusted to reduce potential losses.
4. Improving risk management: Incorporating the risk-reward ratio into trading strategies enhances overall risk management. It prompts traders to use appropriate position sizing, adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels, and maintain a disciplined approach to trading.
Considerations and Limitations
While the risk-reward ratio is a valuable metric, it is important to acknowledge its limitations and consider additional factors in trading decisions. Factors such as market volatility, liquidity, and overall market conditions can impact trade outcomes and should be taken into account alongside the risk-reward ratio.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing the risk-reward ratio in trading can significantly enhance the prospects of long-term profitability. By adopting a systematic and disciplined approach to evaluating and managing risk, traders can make informed decisions, protect capital, and optimize their trading strategies.
30 comments